Elctrochemical Biosensors/Immunosensor
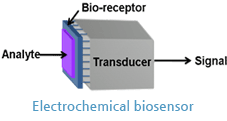
Electrochemical sensor is an analytical device which utilize biological reaction of biomolecules for detecting analyte and it converts a biological response into a quantifiable and processable signal
Cholesterol Sensor
-
Simple and cheap cholesterol biosensor based on poly(thionine)-modified GCE
-
Bo-enzyme modified PTH/GCE
-
Hydroquinone(HQ) redox mediator
-
Excellent stability and recoveries for real sample analysis

Dopamine, Ascorbic Acid, and Uric Acid sensor
-
poly(thionine), poly(chromatope)2B. modified GCE electrode for the detection of dopamine, ascorbic acid,and uric acid.
-
Excellent sensitivity with reasonable detection limit.
-
Graphene based sensors for the selective detection of dopamine, ascorbic acid, and uric acid

Hydroquinone and Catechol Sensors
-
Highly sensitive sensor for the simultaneous detection of hydroquinone(HQ) and catechol(CT) based on poly(thinine)-modified GCE
-
Excellent electrocatalytic activity and reversibility towards the oxidation of both HQ and CT
-
High sensitivity for HQ and CT with nanomolar detection limits


Nitrite Sensor
-
Electrodeposition of sub micrometer size Au particles on transparent FTO for detecting NO2-
-
Highly stable and homogeneous distribution of Au on FTO
-
Sufficiently high catalytic activity toward the oxidation of NO2-
Biomarker sensor
-
CdS-QDs were coupled to an Au nanoimmunosensor on a quartz crystal microbalance(QCM) for annexin A3(ANXA3) detection
-
Covalent immobilization of Anti-ANXA3 antibody
-
Frequency changes induced by the binding of ANXA3 to the anti-ANXA3
-
Simple and label-free DNA sensors based on poly(thionine) modified GCE and Au
-
Immobilization of probe DNA via covalent interaction
-
Excellent selectivites and the sensitivities with picomolar detection limits

